The relationship between diabetes and hypogonadism in males has gained significant medical attention in recent years. With increasing evidence showing that men living with diabetes are more prone to developing low testosterone levels, this condition is now recognized as a critical health concern. Under the guidance of Endocrinologist Dr. Abhishek Shrivastava, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the prevalence, causes, symptoms, and solutions related to hypogonadism in men with diabetes.
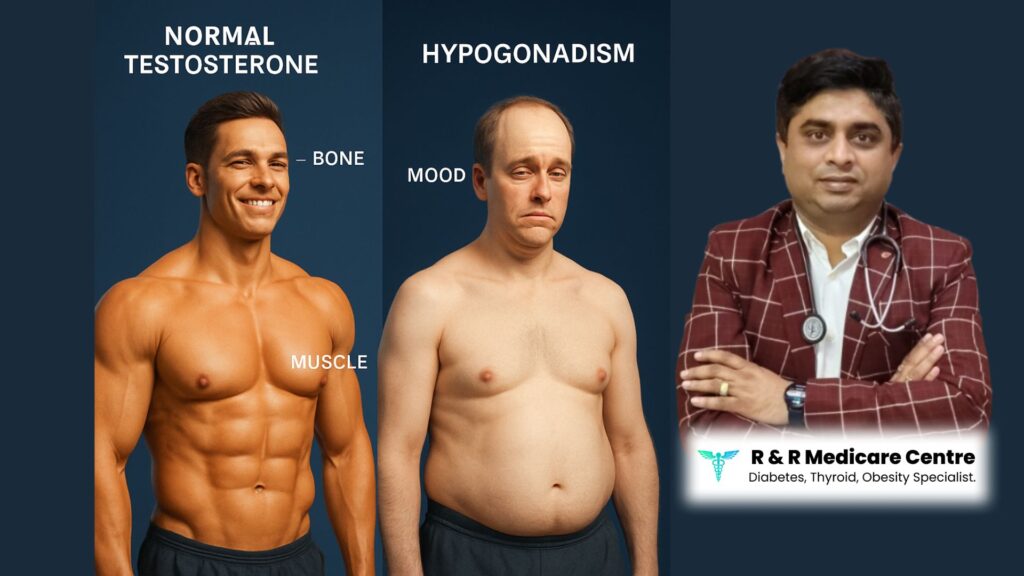
Understanding Hypogonadism in Males
Hypogonadism in males is a medical condition characterized by the body’s inability to produce enough testosterone, the hormone responsible for male sexual and reproductive function. Testosterone plays a vital role in maintaining muscle mass, bone density, red blood cell production, and overall energy levels. When levels fall below normal, men may experience a wide range of symptoms that impact their quality of life.
According to endocrinologist Dr. Abhishek Shrivastava, the prevalence of hypogonadism in diabetic men is significantly higher compared to non-diabetic men. Studies suggest that up to 30–50% of men with type 2 diabetes may suffer from low testosterone, highlighting the strong correlation between these two health concerns.
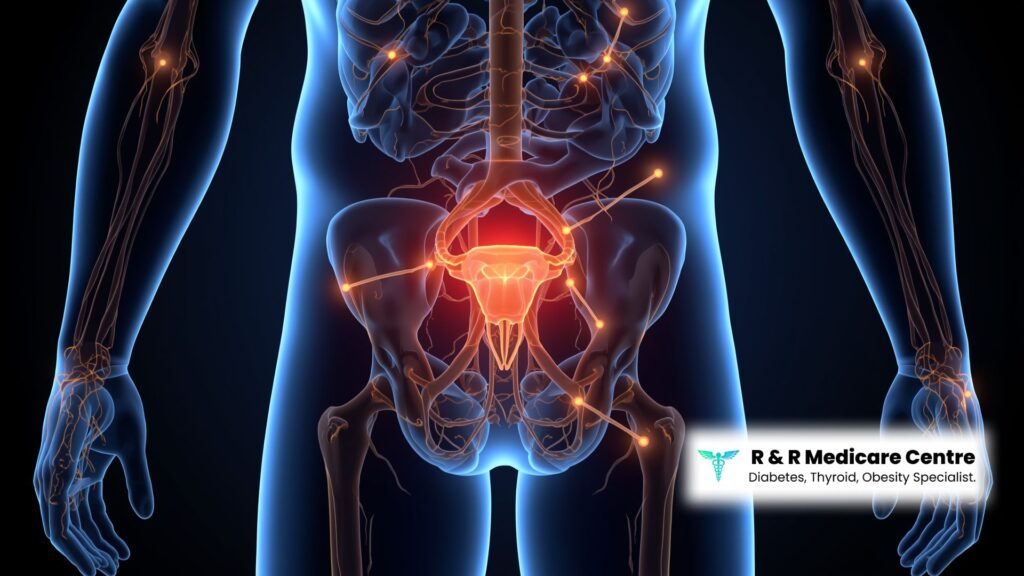
What Is Secondary Hypogonadism?
Secondary hypogonadism occurs when the testicles themselves are capable of producing testosterone but fail to do so due to issues in the pituitary gland or hypothalamus. These glands regulate the release of hormones that signal the testes to produce testosterone. In diabetic men, metabolic changes, obesity, and insulin resistance can interfere with this signaling system, leading to secondary hypogonadism.
Endocrinologist Dr. Abhishek Shrivastava emphasizes that secondary hypogonadism is more common in men with type 2 diabetes because of its strong association with obesity, insulin resistance, and chronic systemic inflammation.
What Causes Hypogonadism?
Hypogonadism can be triggered by various factors:
- Genetic conditions such as Klinefelter syndrome
- Injuries or infections affecting the testes
- Pituitary gland disorders
- Chronic illnesses like diabetes, kidney disease, or obesity
- Medications, especially opioids or steroid treatments
- Aging, which naturally lowers testosterone levels
Among these, diabetes is a major contributor, as it leads to hormonal imbalances, impaired insulin sensitivity, and increased fat accumulation, all of which negatively impact testosterone production.
Does Diabetes Cause Hypogonadism?
Yes. Diabetes directly increases the risk of hypogonadism in males. Clinical research shows that men with diabetes often have reduced testosterone levels compared to men without diabetes. This condition, known as diabetic hypogonadism, is linked with insulin resistance, obesity, and vascular complications.
Endocrinologist Dr. Abhishek Shrivastava explains that diabetes contributes to hypogonadism through multiple pathways:
- Increased abdominal fat leads to higher conversion of testosterone into estrogen.
- Chronic inflammation disrupts hormonal regulation.
- Poor blood circulation impairs testicular function.
- Long-term uncontrolled blood sugar damages the hypothalamic-pituitary axis.
Thus, managing blood sugar effectively is crucial not only for diabetes care but also for maintaining normal testosterone levels.
What Are the Symptoms of Hypogonadism in Males?
The symptoms of hypogonadism in men with diabetes may vary, but they often include:
- Low energy and fatigue
- Reduced muscle strength
- Increased body fat
- Low libido and erectile dysfunction
- Decreased bone density leading to osteoporosis
- Mood swings, depression, and irritability
- Poor concentration and memory issues
- Infertility or reduced sperm count
These symptoms may overlap with common diabetic complications, which is why hypogonadism often goes undiagnosed in men with diabetes. Endocrinologist Dr. Abhishek Shrivastava advises men with persistent symptoms to undergo hormonal testing for early detection and management.
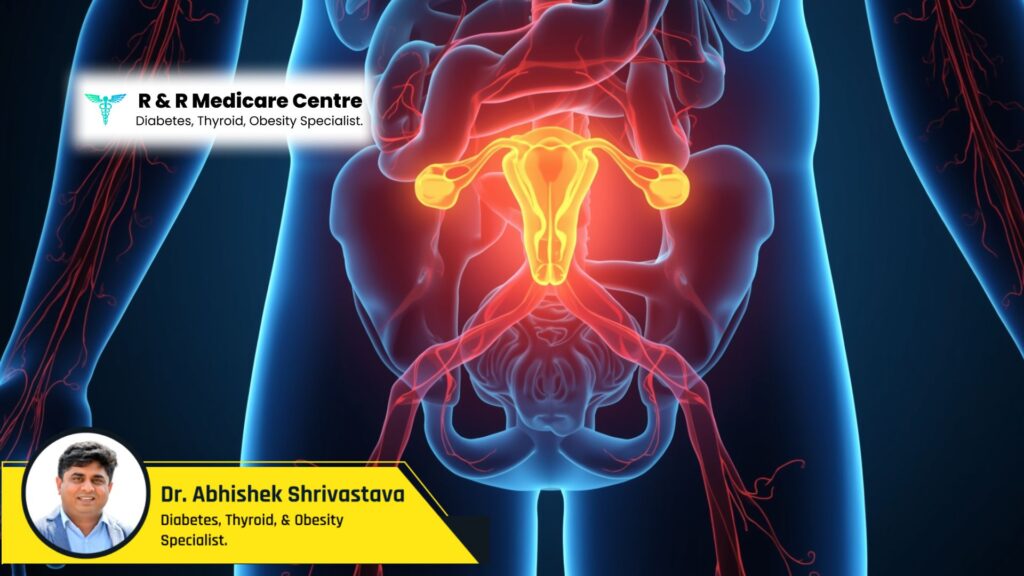
Prevalence of Hypogonadism in Male Diabetes
Studies worldwide confirm the strong connection between diabetes and hypogonadism. Research indicates that:
- Up to 40% of men with type 2 diabetes have low testosterone.
- Diabetic men are twice as likely to suffer from erectile dysfunction due to low testosterone.
- Hypogonadism in diabetic men contributes to worsening insulin resistance, creating a vicious cycle.
- Men with low testosterone are at higher risk of cardiovascular complications, including heart disease and stroke.
Endocrinologist Dr. Abhishek Shrivastava highlights that early diagnosis of hypogonadism in diabetic men is crucial for improving both hormonal balance and overall diabetes management.
Expert Insights by Dr. Abhishek Shrivastava
To answer the most frequently asked questions:
What is hypogonadism in males?
Hypogonadism in males is a condition where the body produces insufficient levels of testosterone, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, sexual dysfunction, and muscle weakness.
What is secondary hypogonadism?
Secondary hypogonadism occurs when the problem lies not in the testes but in the hypothalamus or pituitary gland, which fail to signal testosterone production properly.
What causes hypogonadism?
It can result from genetic disorders, testicular injuries, pituitary dysfunction, chronic illnesses like diabetes, certain medications, or age-related hormonal decline.
Does diabetes cause hypogonadism?
Yes, diabetes is a major risk factor. Poor blood sugar control, obesity, and insulin resistance are directly linked to low testosterone levels in men.
What are the symptoms of hypogonadism in males?
Symptoms include reduced sexual drive, erectile dysfunction, fatigue, muscle loss, weight gain, bone weakness, mood disturbances, and infertility.
Conclusion
The prevalence of hypogonadism in male diabetes is alarmingly high, yet often underdiagnosed. Early recognition and treatment can significantly improve quality of life, prevent complications, and optimize diabetes control. With expert care from specialists like endocrinologist Dr. Abhishek Shrivastava, men can receive accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment, and lifestyle guidance to restore hormonal balance and overall well-being.
